About Mutual TLS
MTLS is a security protocol used to authenticate both the client and the server in a connection, ensuring that both parties are verified before any communication occurs.
In Nuapay’s application, MTLS is employed for two primary purposes:
- Securing incoming API requests.
- Securing outgoing Webhook messages sent back to clients.
This ensures that only trusted clients can make requests, and that Webhook updates are delivered securely to authenticated recipients, maintaining data integrity and confidentiality in both directions.
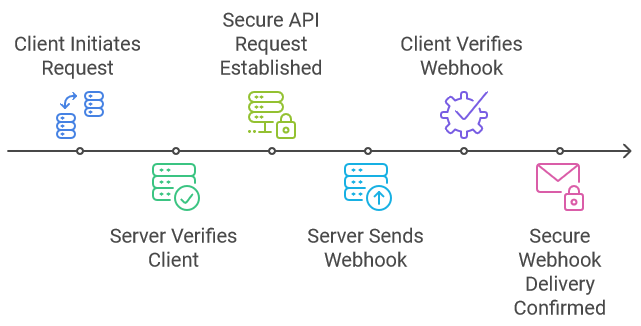
MTLS is especially useful if you are deployed in the cloud and your source IP addresses are subject to change.
Certificates
Certificates play a crucial role in MTLS, authenticating both the client and the server. Each party (client and server) is issued with a certificate, which contains a public key and other identifying information. When a connection is established, both parties exchange their certificates and use the corresponding private keys to prove their identity.
In Nuapay:
- Incoming API Requests: The client presents its certificate when initiating a request. Nuapay verifies the certificate, ensuring the client is trusted. Simultaneously, Nuapay presents its own server certificate to the client, ensuring the client can verify the server’s authenticity.
- Outgoing Webhook Messages: When Nuapay sends a Webhook update, it presents its server certificate to the client. The client, in turn, presents its certificate to verify it is the intended recipient of the message. This mutual authentication ensures both the source and destination are legitimate.
Certificates are issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs) and can be revoked or expired, providing an additional layer of security and control.
Certificate Generation
Before configuring MTLS you must first generate a certificate. This process is outside the scope of this documentation.
There are various online tools, however, that allow you to do this (https://en.rakko.tools/tools/46/, for example).
MTLS Configuration
MTLS may be configured in two ways, via: